Overview
Teaching: 5 min Exercises: 5 minQuestions
What functionality does the xarray library offer?
What are the benefits and limitations of this library?
What is the fundamental architecture of xarray data objects?
Objectives
learning the xarray data model
selection and subsetting of array datasets using labeled indexing
What is xarray?
- originally developed by employees (Stephan Hoyer, Alex Kleeman and Eugene Brevdo) at The Climate Corporation
- xaray extends some of the core functionality of the Pandas library:
- operations over named dimensions
- selection by label instead of integer location
- powerful groupby functionality
- database-like joins
When to use xarray:
- if your data are multidimensional (e.g. climate data: x, y, z, time)
- if your data are structured on a regular grid
- if you can represent your data in netCDF format
Basic xarray data structures:
- NetCDF forms the basis of the xarray data structure
- two main data structures are the
DataArrayand theDataset
DataArray
- the
DataArrayis xarray’s implementation of a labeled, multi-dimensional array - the
DataArrayhas these key properties:data: N-dimensional array (NumPy or dask) holding the array’s values,dims: dimension names for each axis,coords: dictionary-like container of arrays that label each point, andattrs: ordered dictionary holding metadata
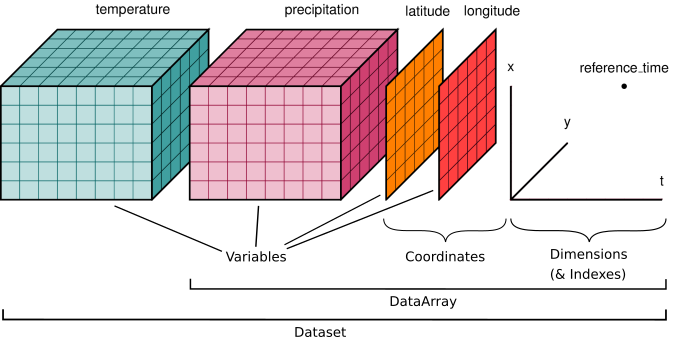
- dimensions (x, y, time); variables (temp, precip); coords (lat, long); attributes
Dataset
- xarray’s multi-dimensional equivalent of a Pandas
DataFrame - dict-like container of DataArray objects with aligned dimensions
- Datasets have these key properties:
dims: dictionary mapping from dimension names to the fixed length of each dimension,data_vars: dict-like container ofDataArrayscorresponding to data variables,coords: dictionary-like container ofDataArraysintended to label points used in data_varsattrs: ordered dictionary holding metadata
begin by importing the xarray library
import xarray as xrOpen the dataset
First we open the data and load it into a Dataset. (Note: the choice of engine depends on the format of the netCDF file. See our dataset description lesson).
ds = xr.open_dataset('../data/airtemp_global.nc')
(NOTE: here and elsewhere, replace <rootDir> with the full path to your own data directory)
You’ll notice this seemed to go very fast. That is because this step does not actually ask Python to read the data into memory. Rather, Python is just scanning the contents of the file. This is called lazy loading.
Dataset Properties
Next we will ask xarray to display some of the parameters of the Dataset. To do this simply return the contents of the Dataset variable name:
ds

Displaying
DatasetpropertiesTry looking up the coordinates (coords), attributes (attrs) and data variables (data_vars) for our existing dataset. Look at the output and think about what this tells us about our sample dataset.
Extracting DataArrays from a Dataset
We have queried the dataset details about our Datset dimensions, coordinates and attributes. Next we will look at the variable data contained within the dataset. In the graphic above, there are two variables (temperature and precipitation). As described above, xarray stores these observations as a DataArray, which is similar to a conventional array you would find in numpy or matlab.
Extracting a DataArray for processing is simple. From the Dataset metadata shown above, notice that the name of the climate variable is ‘t2m’ (2 meter air temperature). Suppose we want to extract that array for processing and store it to a new variable called temperature:
temperature = ds['t2m']
Now, take a look at the contents of the temperature variable. Note that the associated coordinates and attributes get carried along for the ride. Also note that we are still not reading any data into memory.
Key Points
xarray is build on the netCDF data model
xarray has two main data structures: DataArray and Dataset
DataArrays store the multi-dimensional arrays
Datasets are the multi-dimensional equivalent of a Pandas dataframe